Additive Manufacturing
Immensa utilizes the “digital twins” of physical spare parts to offer on-demand additive manufacturing services that leverage advanced technologies like digital warehousing to provide a faster, more sustainable option that reduces carbon emissions from production to logistics.
100,000+
Parts produced to date
2 Factories
State-of-the-art centres
in the UAE and KSA
Shorter Lead Times
For manufacturing and logistics
Resilient Supply Chain
Through decentralized and
localized production

Reduced Manufacturing and Storage Costs
Through efficient material usage and on-demand production

Innovative Manufacturing Capabilities
For complex geometries and specialized materials
Spare Part Categories
Here are some of the spare part types that can be manufactured on demand with Immensa.
*Production time and costs compared to conventional methods
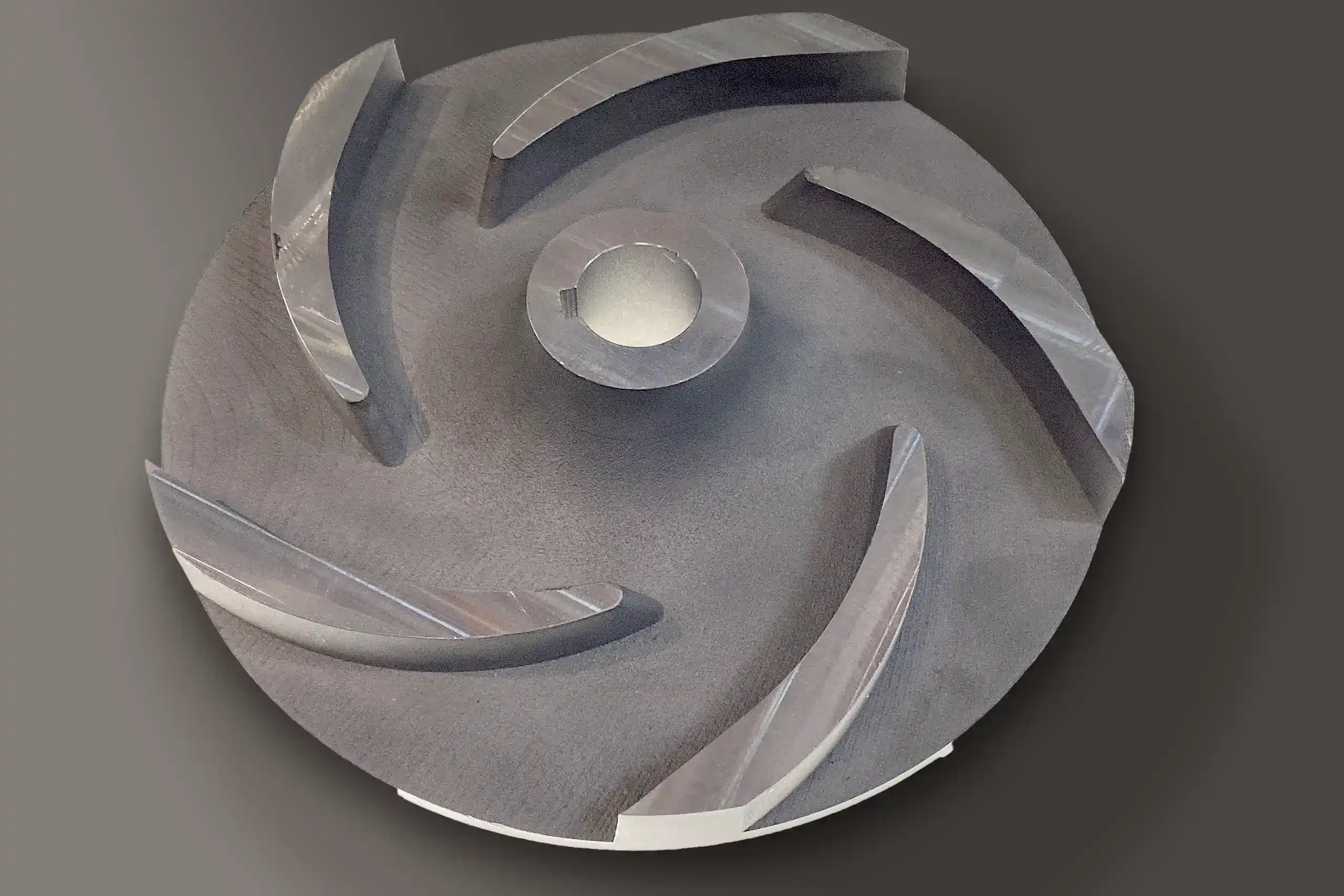

Open Impellers
Material: Metal
Dimensions: 150 x 32 mm
- Lead Time
- Cost
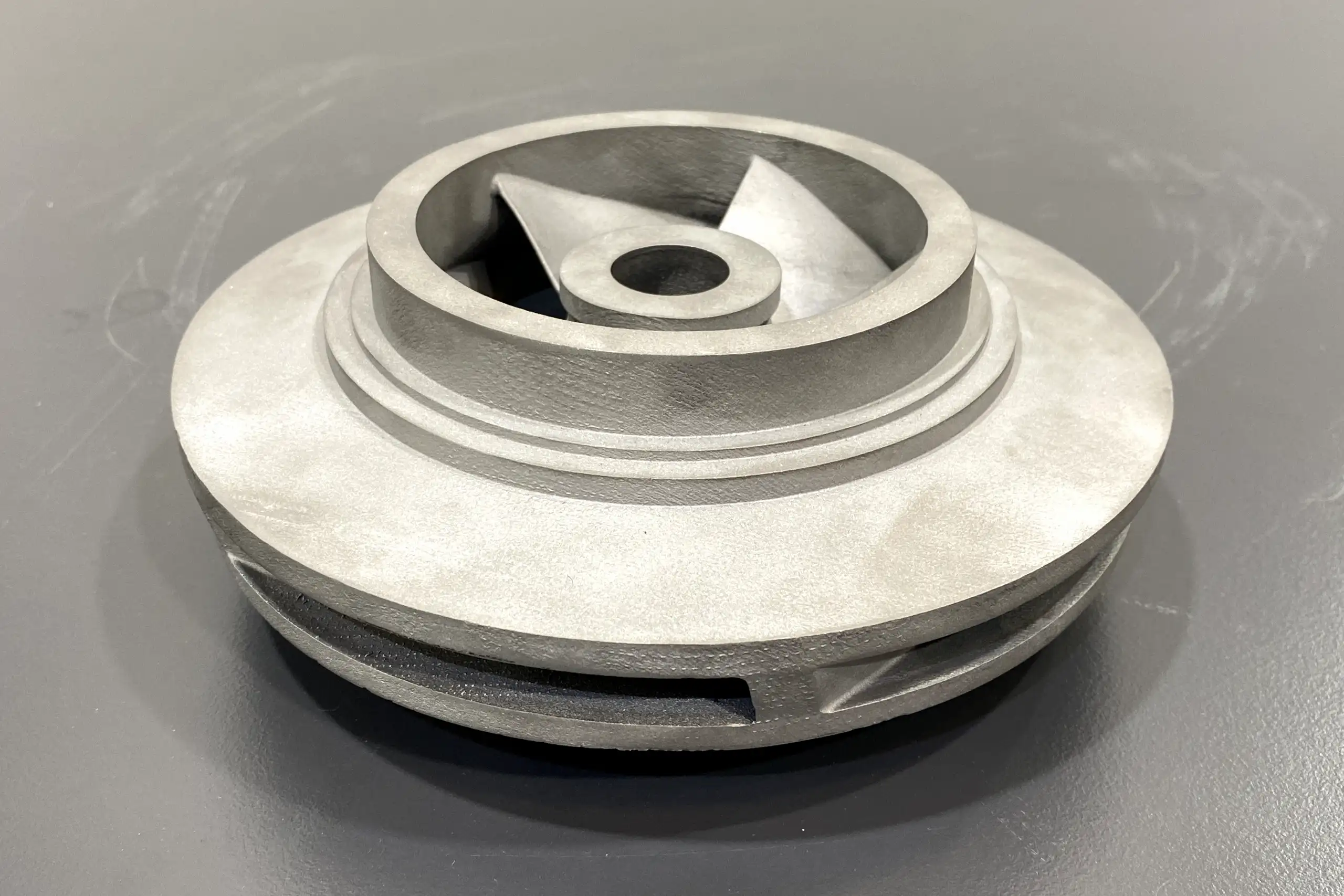

Closed Impellers
Material: Metal
Dimensions: 178 x 60 mm
- Lead Time
- Cost
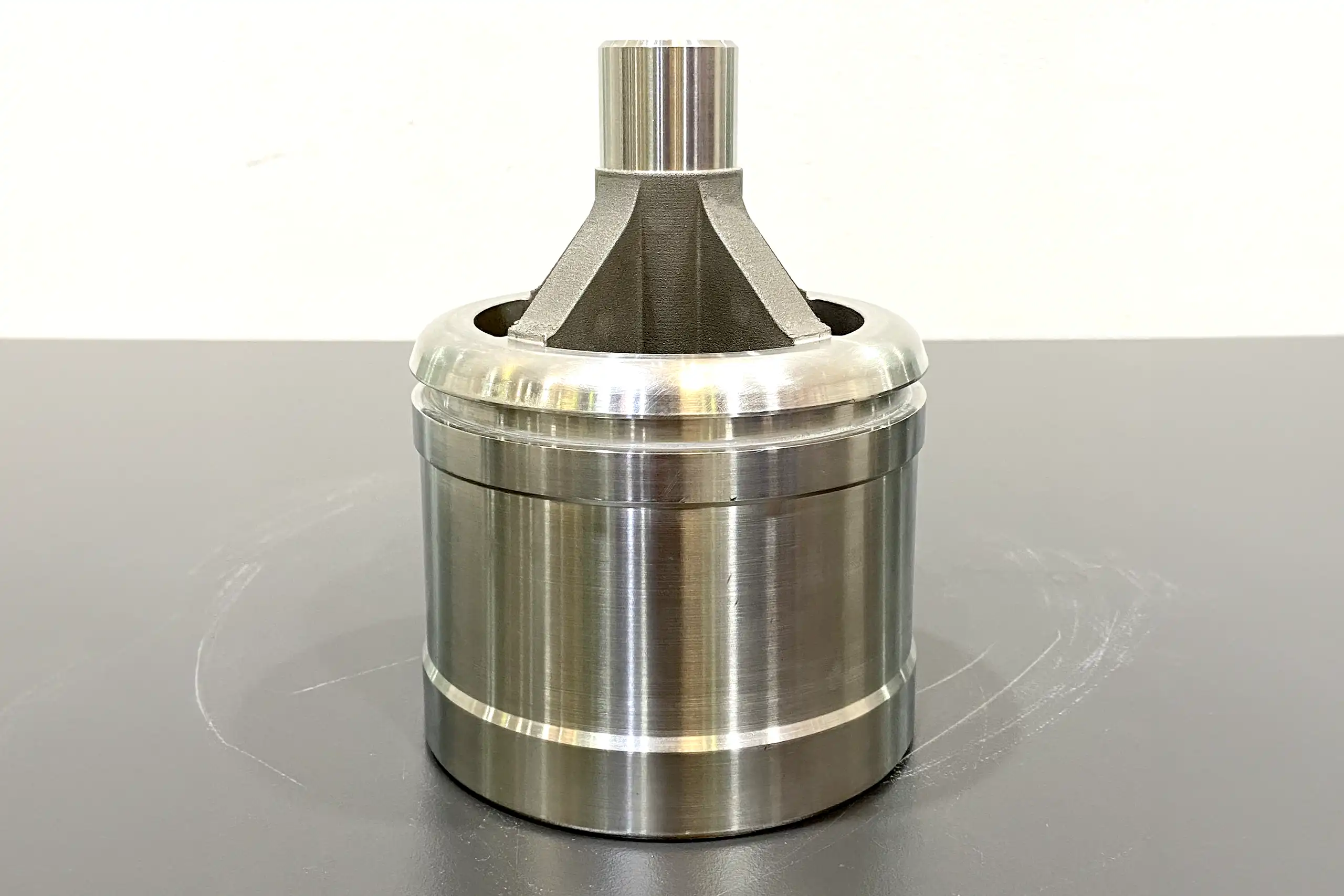

Plugs
Material: Metal
Dimensions: 128 x 173 mm
- Lead Time
- Cost
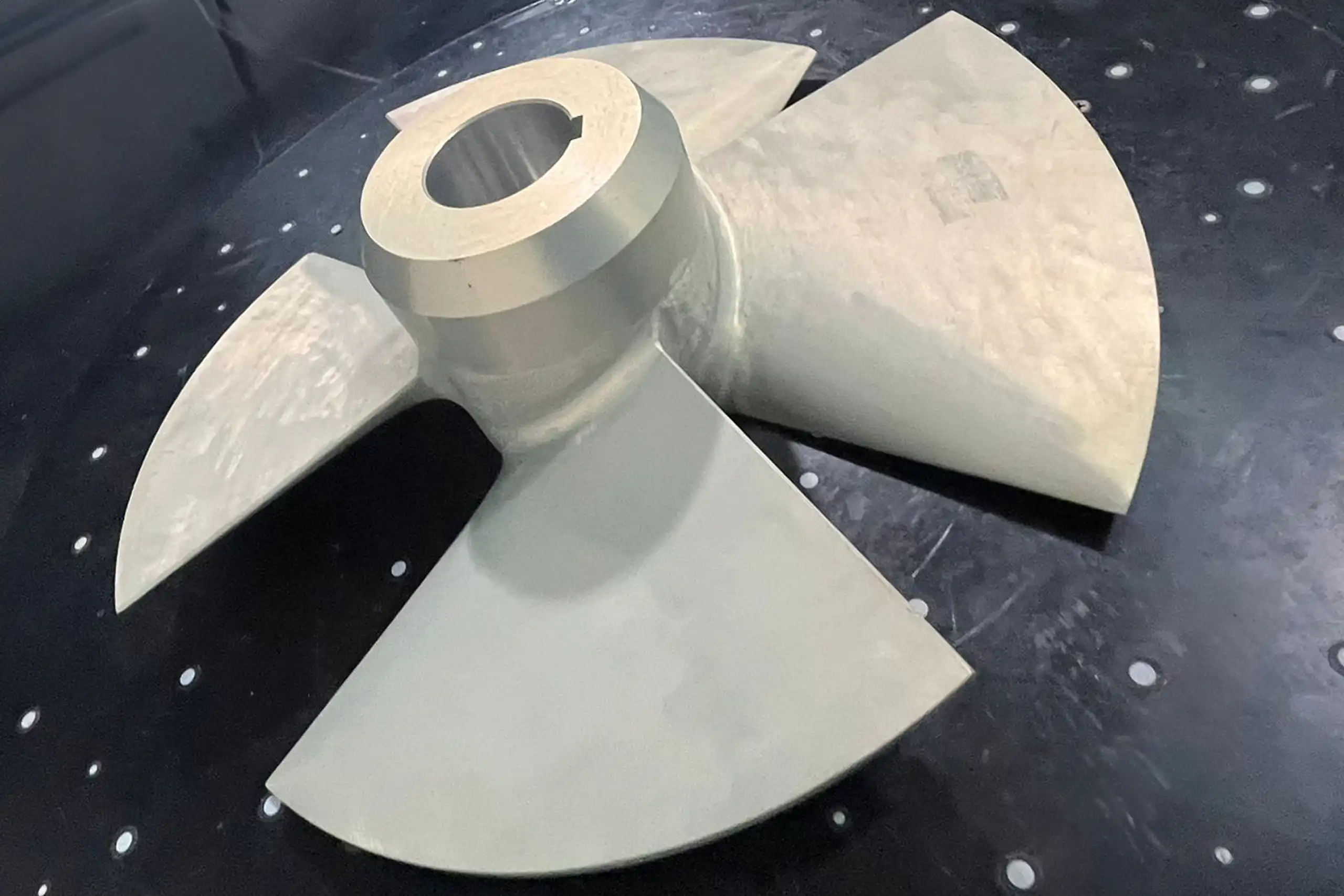
Inducers
Material: Metal
Dimensions: 202 x 47 mm
- Lead Time
- Cost
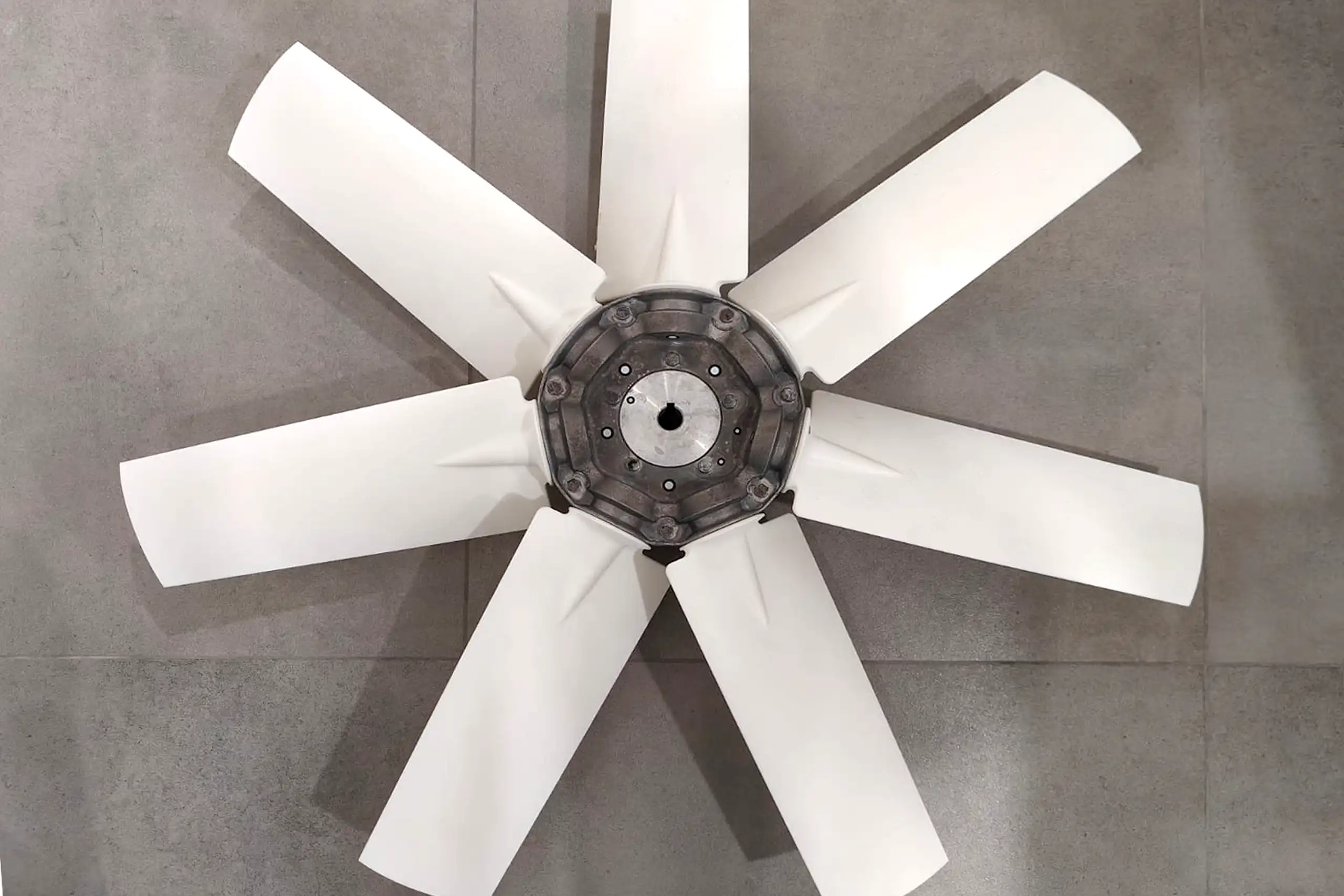

Fans
Material: Polymer
Dimensions: 800 x 100 mm
- Lead Time
- Cost
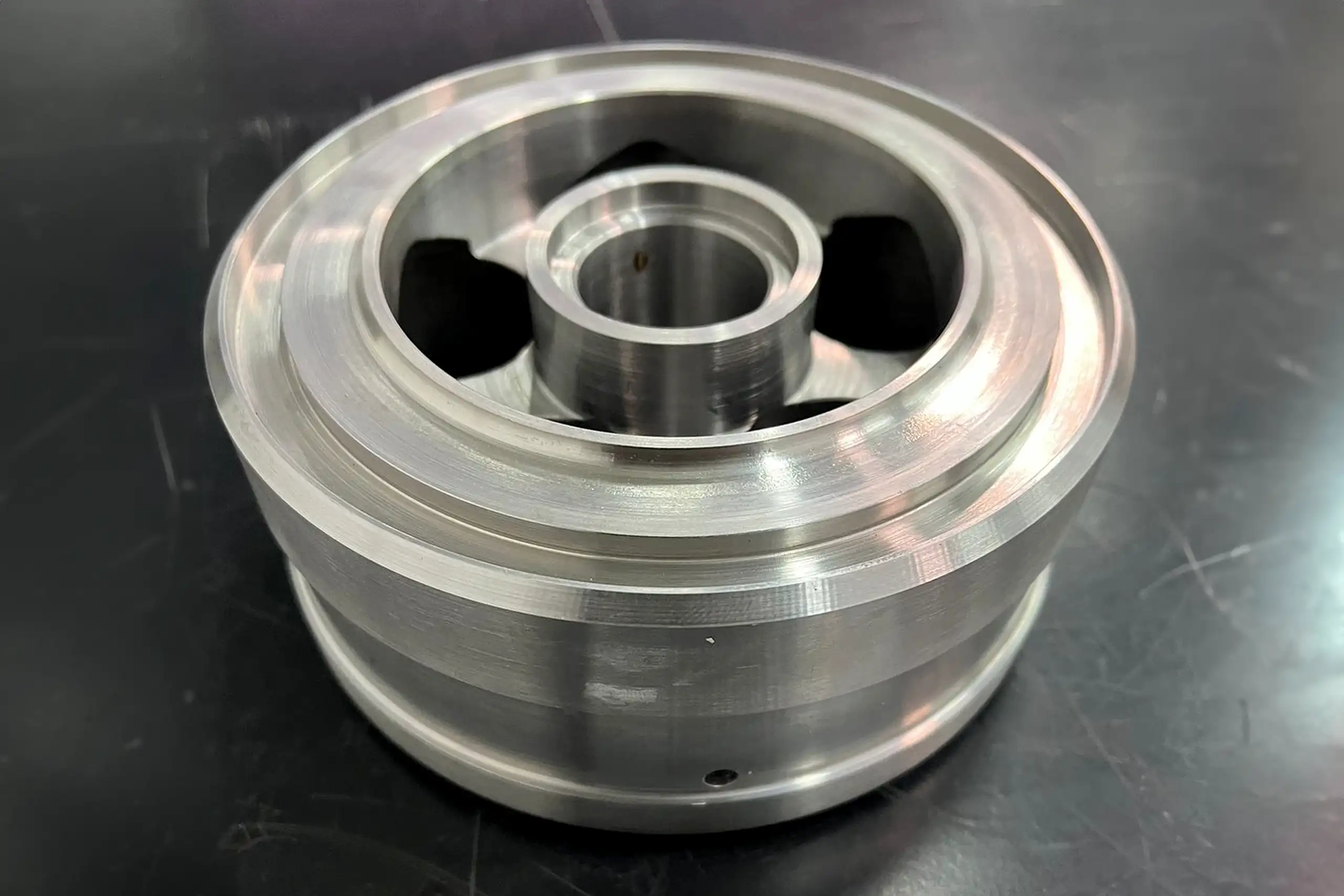

Seats
Material: Metal
Dimensions: 149 x 81 mm
- Lead Time
- Cost
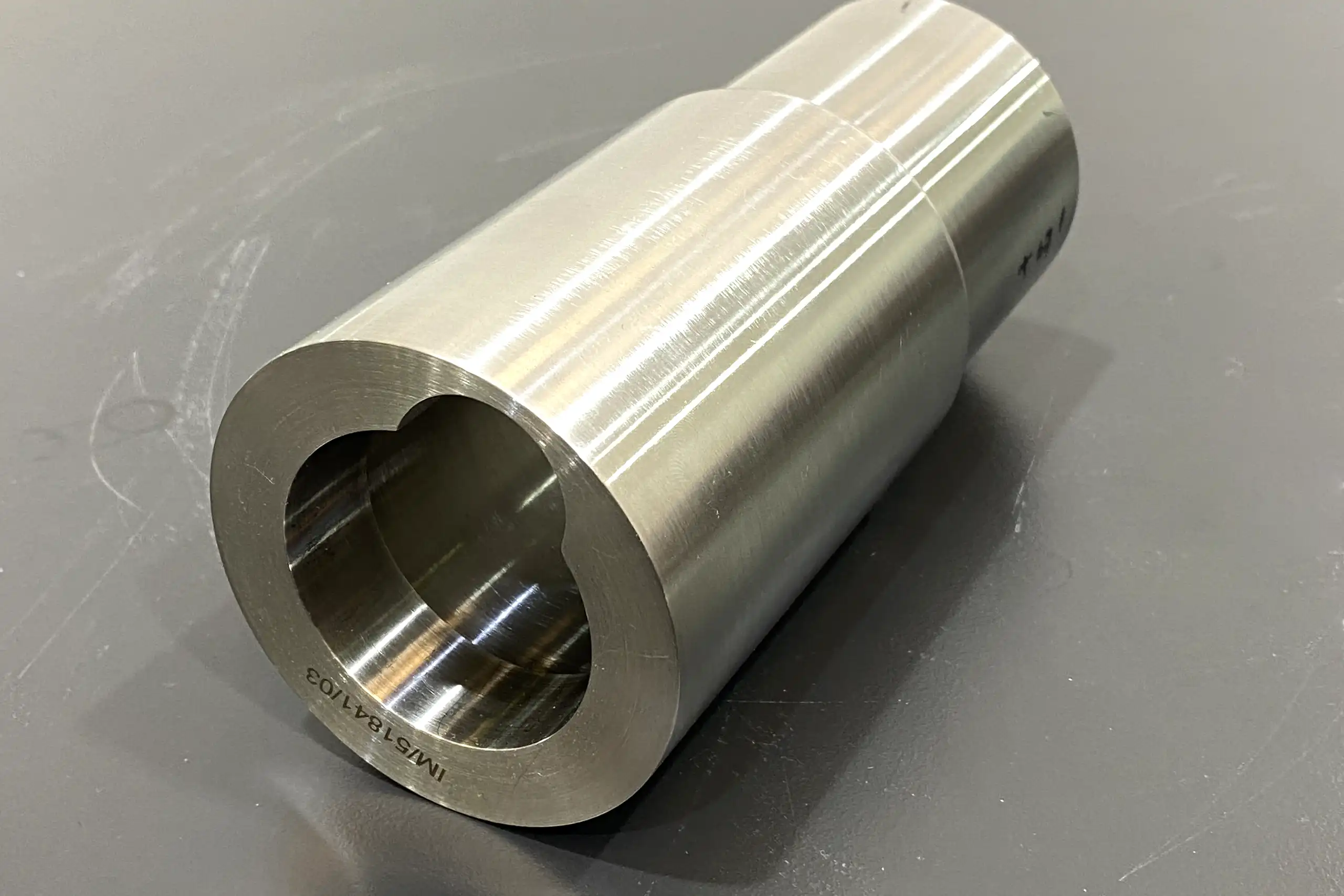

Bushings
Material: Metal
Dimensions: 72 x 161 mm
- Lead Time
- Cost
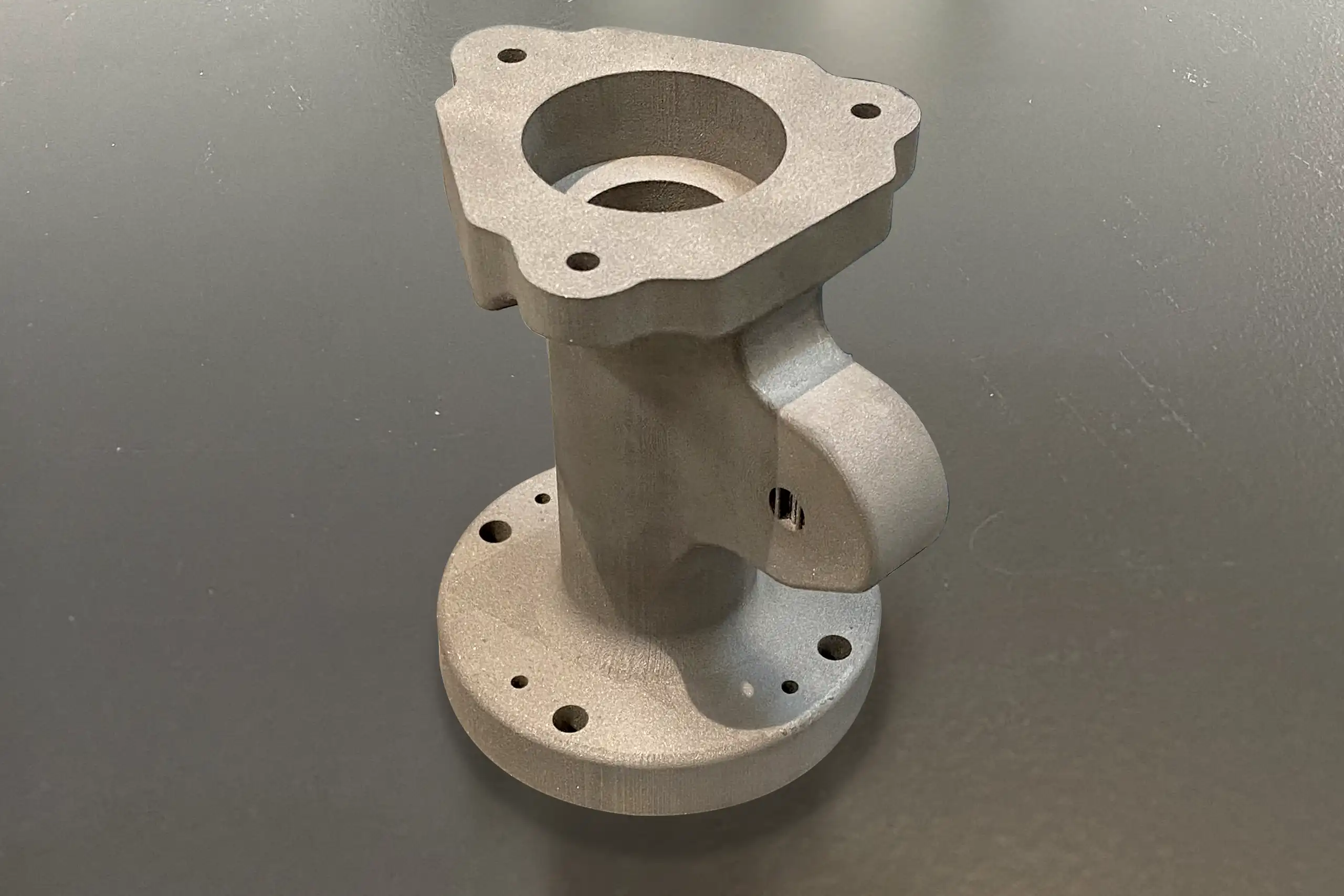

Flanged Pipes
Material: Metal
Dimensions: 136 x 127 x 105 mm
- Lead Time
- Cost
3D Printing Methods
Direct Metal Laser Melting (DMLM)
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
Stereolithography (SLA)
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM)
Direct Metal Laser Melting (DMLM)
Melts metal powder with a laser to create fully dense metal parts for high-performance oil and gas applications.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
Fuses together polymer or metal powder particles with a high-powered laser. Ideal for complex geometries and small batch production.
Stereolithography (SLA)
Solidifies layers of liquid resin with a UV laser. Allows for high precision printing of intricate parts with smooth surface finishes.
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
Extrudes polymer and thermoplastic material to produce durable, functional parts with strong interlayer adhesion.
Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM)
Deposits layers of metal wire that is melted by an electric arc to create robust and large-scale parts.
Materials

Metal
Stainless Steel (316L)
Stainless Steel (17-4PH)
Super Duplex 2507
Stainless Steel 410
Stainless Steel 420
Inconel (IN625)
Inconel (IN718)
Titanium (Ti-6Al-4V)
Maraging Steel MS1 (M300)
Cobalt Chromium
Aluminum (AlSi10Mg)
Polymer
ABS
PA 11 / PA 12
PEEK
Carbon Fiber PEEK
PETG
PLA
Ultem
High Temperature Resin
Tough Resin
Rigid Resin
Post-processing
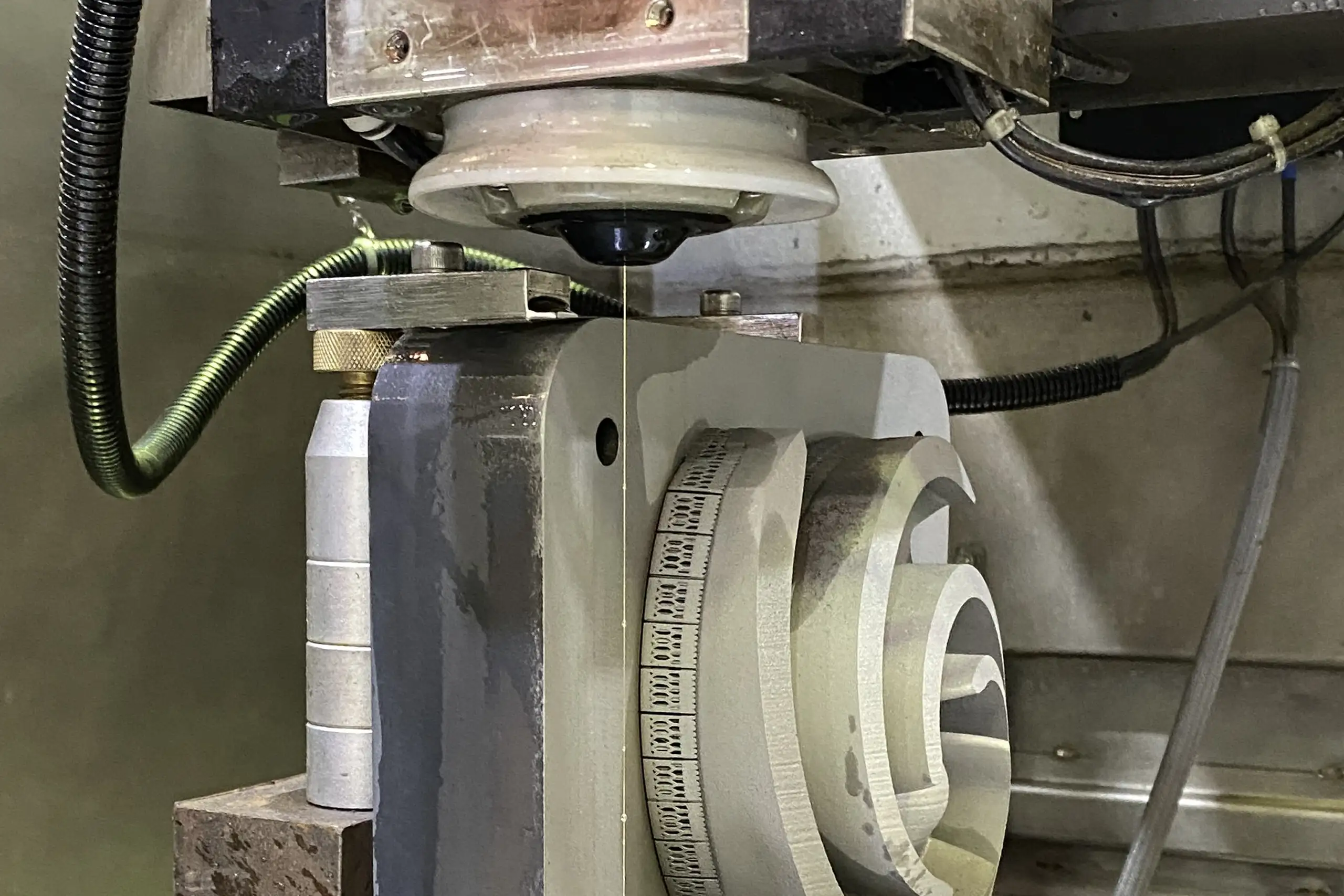
Wire EDM Cutting
Refines intricate features for metal spare parts by removing excess material using precise electrical charges.
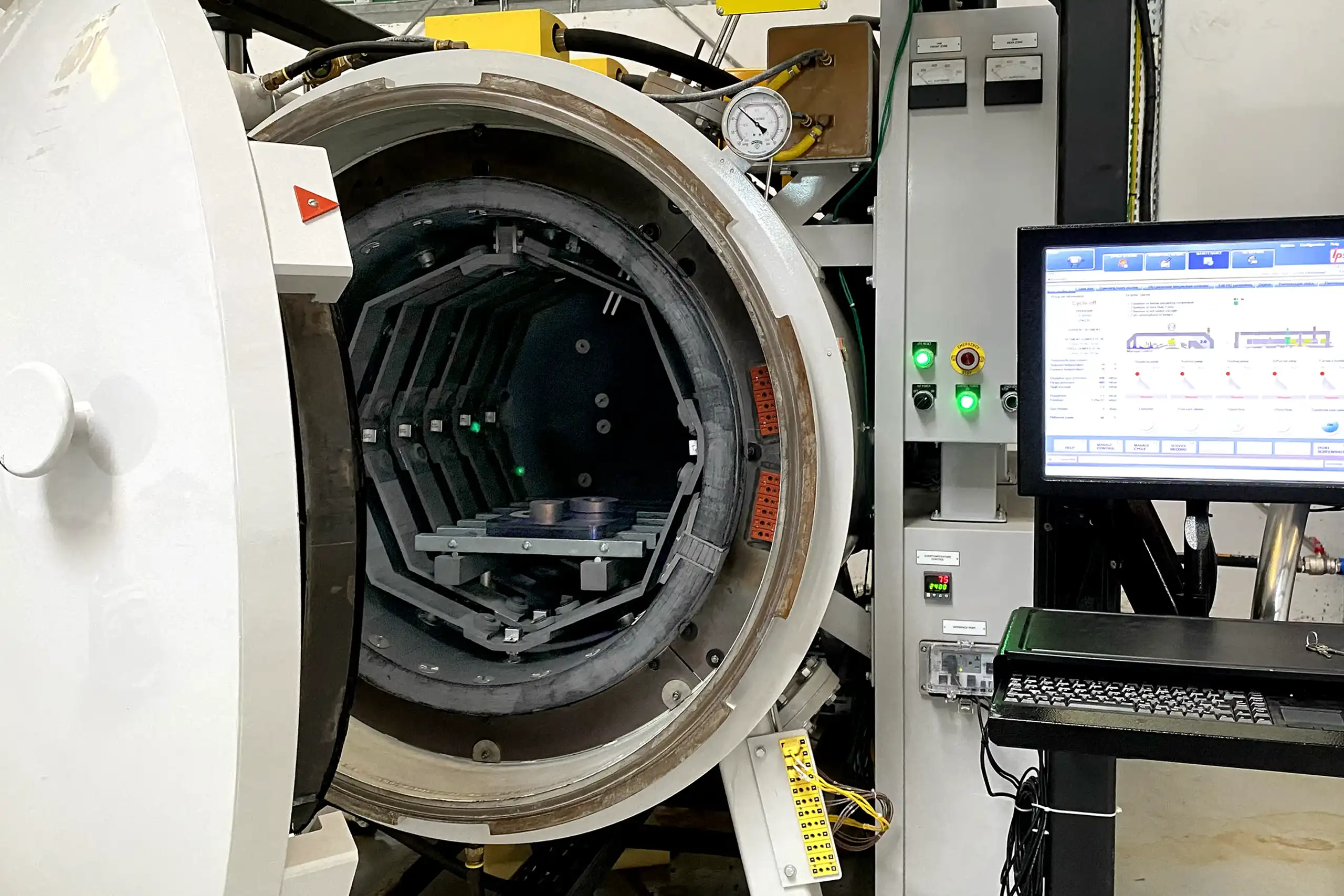

Heat Treatment
Applies controlled heat to 3D printed spare
parts to improve mechanical properties.
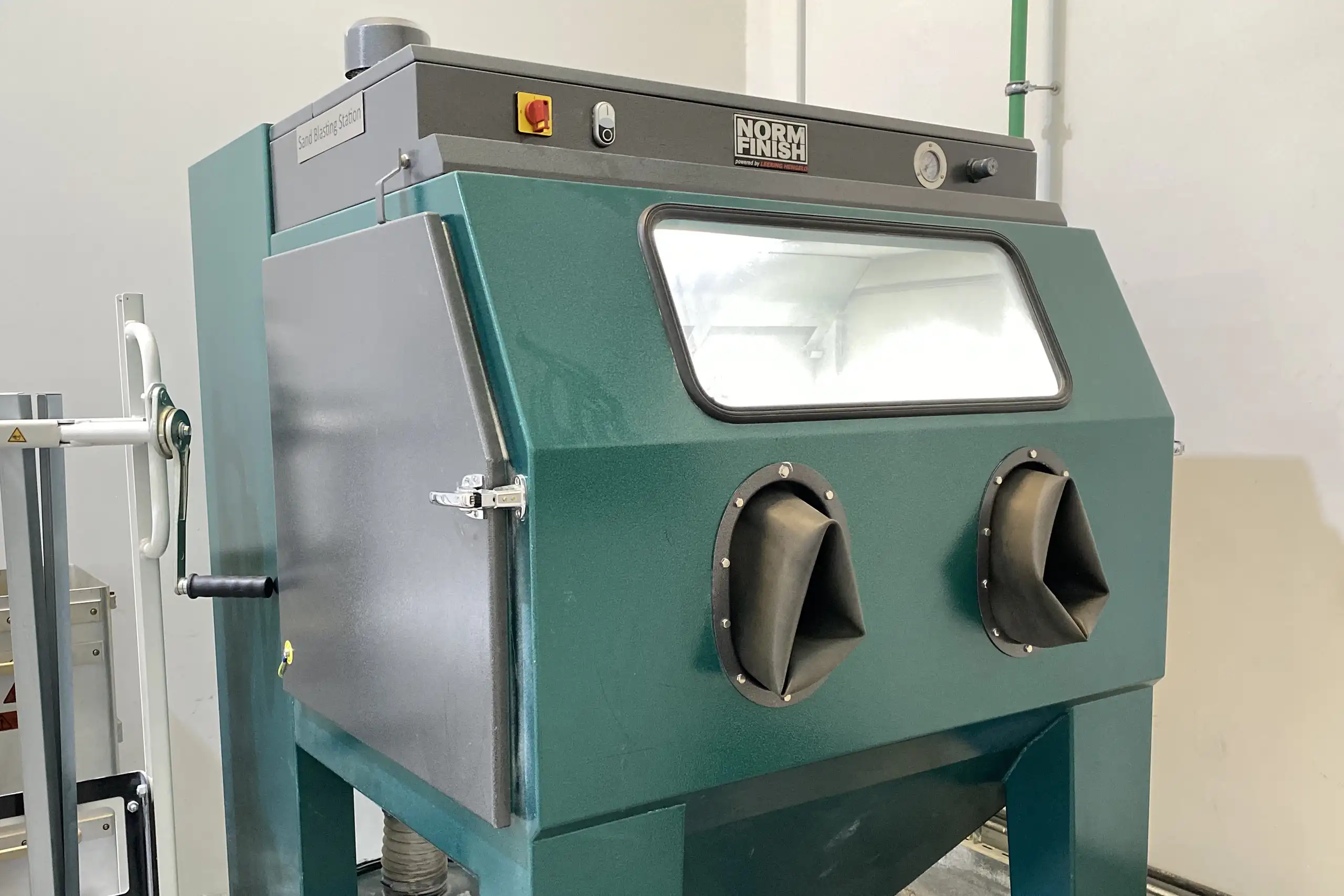

Sandblasting
Removes residual powders, debris, or contaminants from the surface of the printed parts by using abrasive materials.
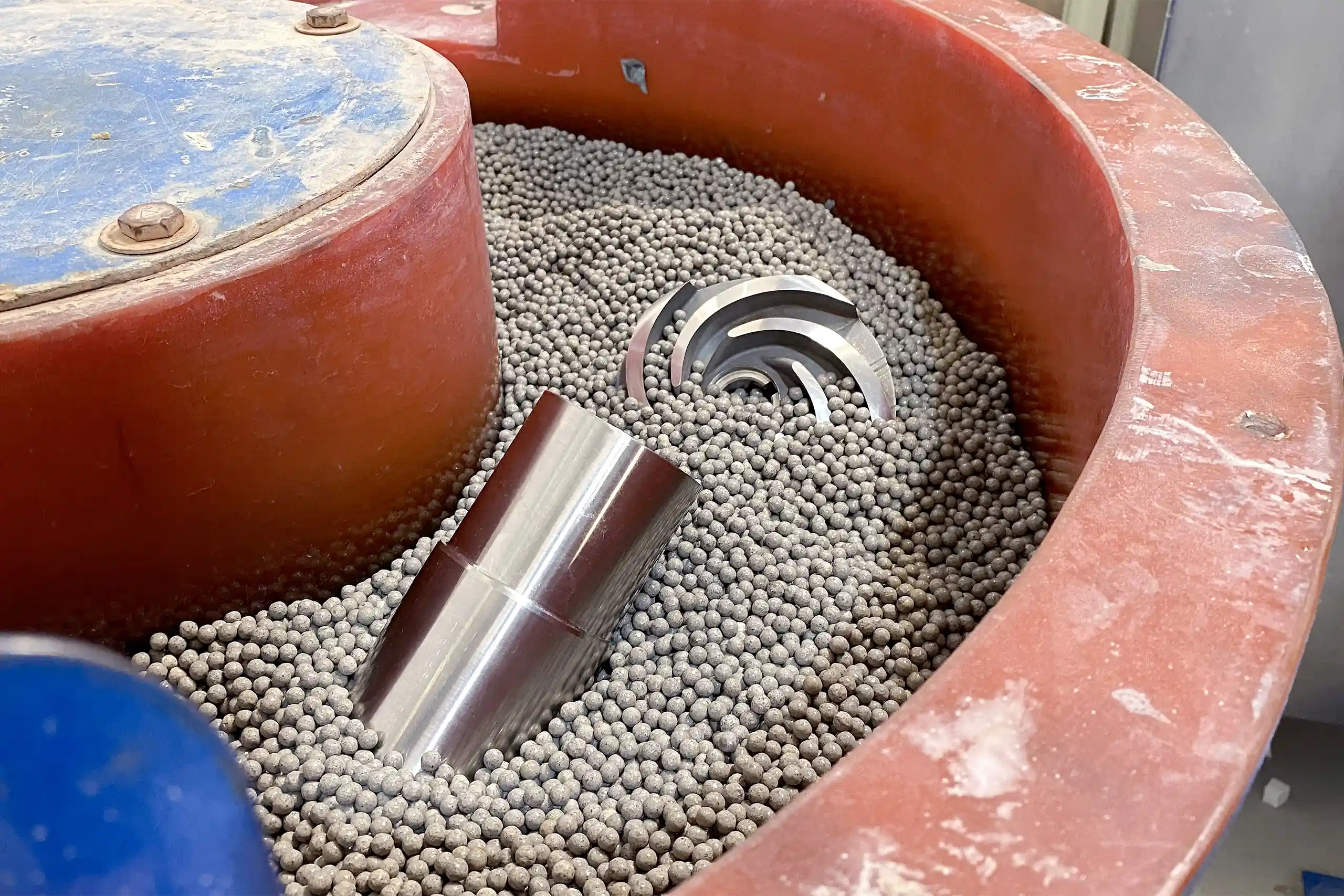

Vibro Polishing
Improves surface finish by vibrating abrasive materials against the printed part
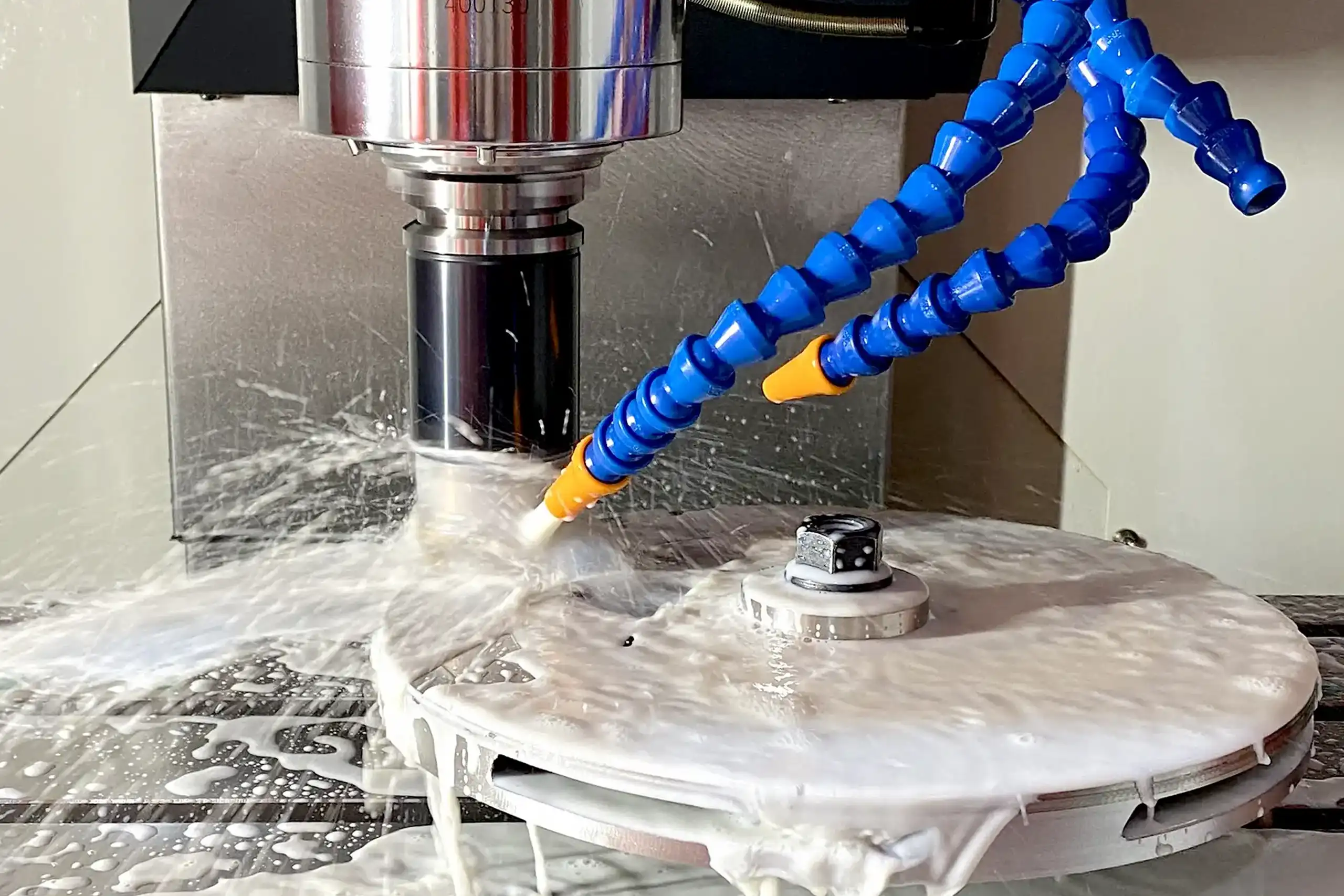

CNC Machining, Turning, & Milling
Removes excess materials and refines the shape of printed spare parts by utilizing different cutting tools.
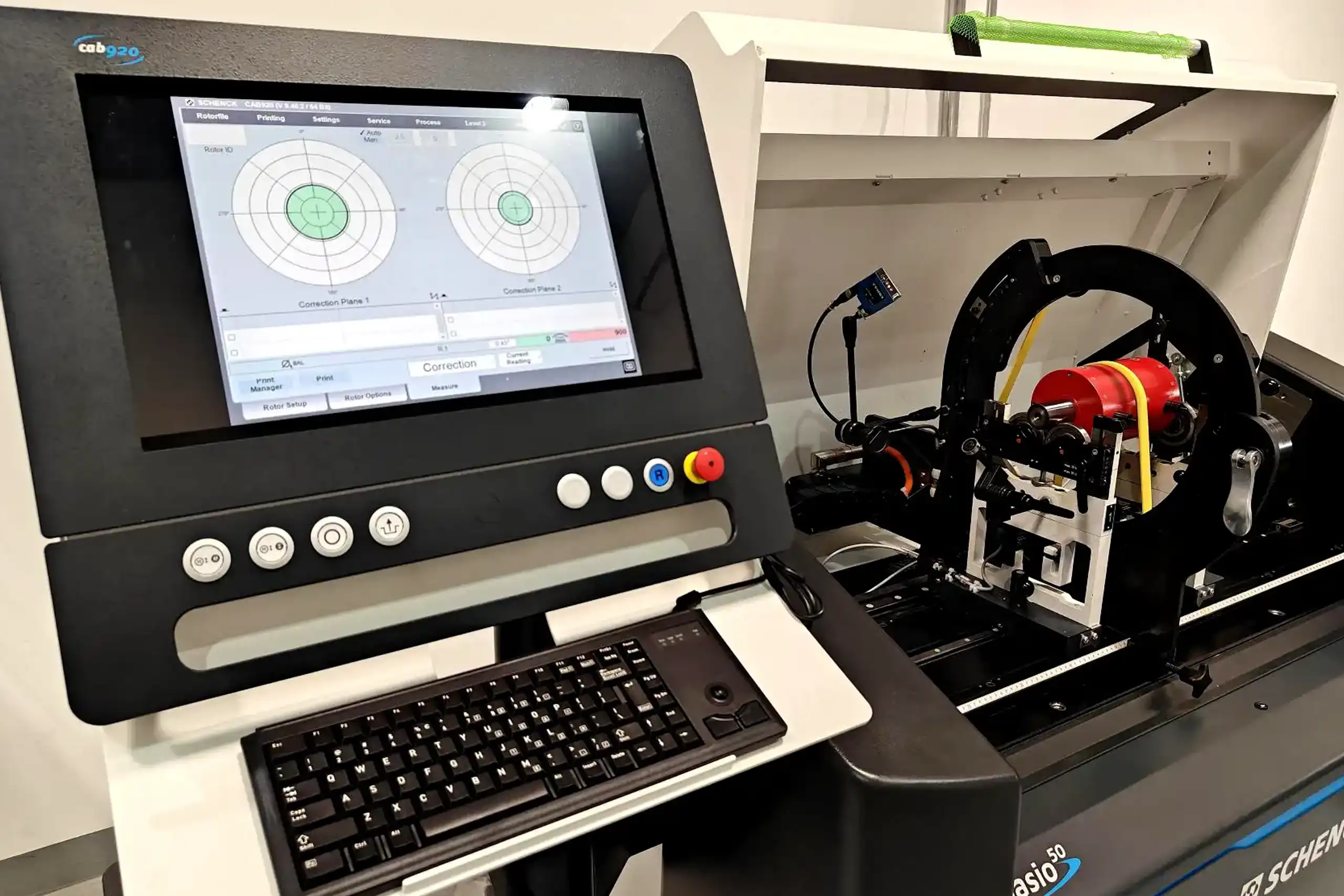

Balancing
Ensures even mass distribution of rotary parts to enhance performance, longevity, and safety of rotary machinery.
Quality Control
Inspections & Testing
- Dye Penetrant Test
- X-ray Radiography
- CT scan
- Ultrasonic Flaw Detection
- Chemical Composition Testing
- Micro & Macro-structure Examination
- Hardness Testing
- Tensile Testing
- Impact Testing
- Fatigue Testing
- Corrosion Testing IGC
- Fracture Toughness
- CMM Inspections
- HIC (as per NACE TM0284)
- SSC Four Point Bend (as per NACE TM 0177 & ASTM G39)
- 3D Inspection with Laser Scanning
Frequently
Asked Questions
What is additive manufacturing?
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, is an advanced manufacturing process that creates three-dimensional objects layer by layer.
It offers the ability to produce intricate, customized, and complex parts with high precision, more efficient material usage, and reduced energy consumption compared to conventional manufacturing methods.
How much lead time does it usually take to produce a functional spare part?
The full production and post-processing time depends on the size, material, and complexity of the needed part.
For example, a 50mm stainless steel cube will take less than an hour of printing time, not including the required post-processing steps. And a stainless steel closed impeller with an outer diameter (OD) of 150mm can be completely manufactured within 3 to 4 days.
What are the material options for manufacturing?
Kindly refer to the Materials section of this page. For unlisted materials, you may send a message to our team.
How reliable are the 3D printed parts compared to conventionally manufactured ones?
3D printed metal parts display the same characteristics that conventionally manufactured parts have. In most cases, parts produced through metal additive manufacturing prove to be stronger than conventional counterparts.
With Immensa’s DNV certifications for additive manufacturing, our 3D printed spare parts are produced to the highest industry standards to ensure reliability, even for the most demanding applications.
How do you ensure the quality, integrity, and performance of 3D printed spare parts, including the internal features?
Immensa is DNV-certified for additive manufacturing and conducts in-house testing for dimensional accuracies and other NDTs (non-destructive tests). Test coupons are also printed alongside each spare part to validate material properties.
Resources
Additive Manufacturing of Titanium Impellers
Applying additive manufacturing (AM) to oil and gas spare parts supply chains unlocks multiple advantages, including operational, financial, and environmental benefits. AM technologies can enhance existing supply chains and eliminate the need to stock up on physical...
Towards a Sustainable Industry
This whitepaper highlights the significant role of Digital Warehousing and Additive Manufacturing in advancing the sustainability of industrial supply chains, with a special focus on the energy sector. It details how these technologies collectively reduce carbon...


