Dubai today is a major international trading hub and is the center of global supply value chain ranking as one of the 10 most preferred maritime hubs globally. Global companies large and small use Dubai to establish their regional head offices and more importantly as their regional storage and warehousing hub. Jebal Ali Free Zone, Dubai Airport Free Zone, Dubai World Central, and others, have made the transport and storage sector (logistics) the second largest contributor to Dubai’s GDP at 11.8%.
Dubai’s logistics sector which has flourished as a result of an excellent air, sea and land transport capabilities, combined with its strategic location between East and Western Europe, is the basis for its growing industrial transformation. To continue its position as a leading hub, Dubai continues to evolve and embrace disruptive technologies. His Highness Sheikh Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum launched the ‘Dubai 3D Printing Strategy’, a unique global initiative that aims to exploit Additive Manufacturing technology and promote the status of the UAE and Dubai as a leading hub of 3D printing. The strategy adopts an emerging technology that will restructure economies and labor markets and redefine productivity.
3D PRINTING AND THE LOGISTICS INDUSTRY
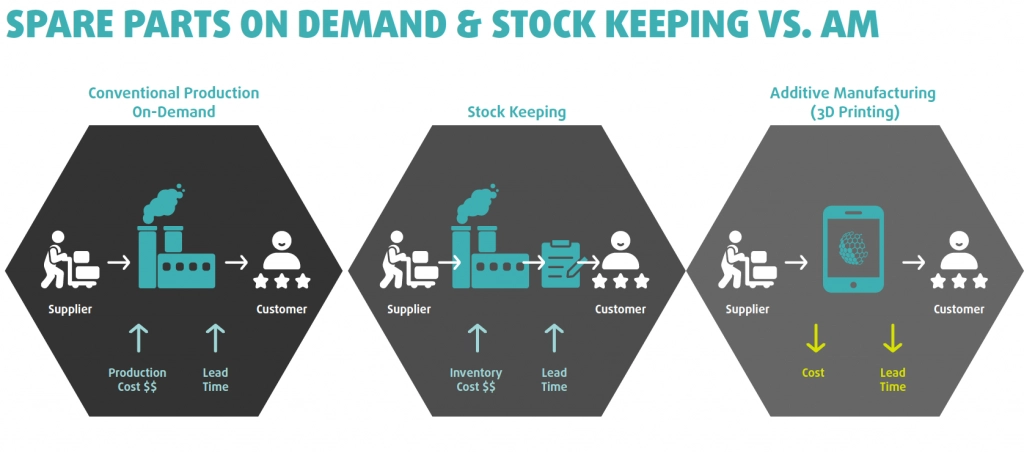
3D Printing has been identified as one of the major disruptive trends to impact the logistics industry in the near future according to DHL as quoted in their report “A DHL perspective on the state of 3D printing and implications for logistics”. As the nature of logistics sector evolves, we will notice corporations transform their supply chains from the conventional central production set-ups to localized production in close proximity to the end-user. 3D Printing facilitates this seismic shift in manufacturing because it offsets the advantage of central production (volume production) by leveraging its agility of production. What that means, is that with additive manufacturing, a company can produce hundreds of different parts on the same machine simultaneously with no minimum quantity required. While in conventional manufacturing, a company has to commit large resources to set-up production line that is typically able to produce the same unit in large quantities and changing the part is costly and time-consuming.
Think of a time when your car broke down and you need a new part installed. Your mechanic had to order the part from the OEM, who then went ahead and produced the part, packed it, and then ship it. It arrives, your mechanic picks it up and proceeds with its installation. Now imagine, your mechanic sends an email to the OEM, who sends back by email a file that has the part in digitized format ready for 3d printing. Your mechanic puts the file to be 3d printed and within hours your part is ready and goes into installation. Instead of weeks, your car is ready in a day or two. Instead of paying for shipping, handling customs, you have it produced right then and there. This applies across all sectors and all businesses, this is not the future, companies have started doing this. Mercedes began rolling out its 3d printed spare parts 2 years ago, starting with plastic parts and moved now to metal spare parts.
DIGITAL INVENTORY SERVICES AND ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING
Virtual or digital inventory can sometimes seem like a magical solution. It means holding digital assets in inventory and producing on-demand, using additive manufacturing. This cuts many costs. The expense of creating initial physical inventory is slashed almost entirely, while that of maintaining the inventory (including logistics, shipping, customs and overheads) is greatly reduced. Moreover, obsolescence and write-offs become a thing of the past.
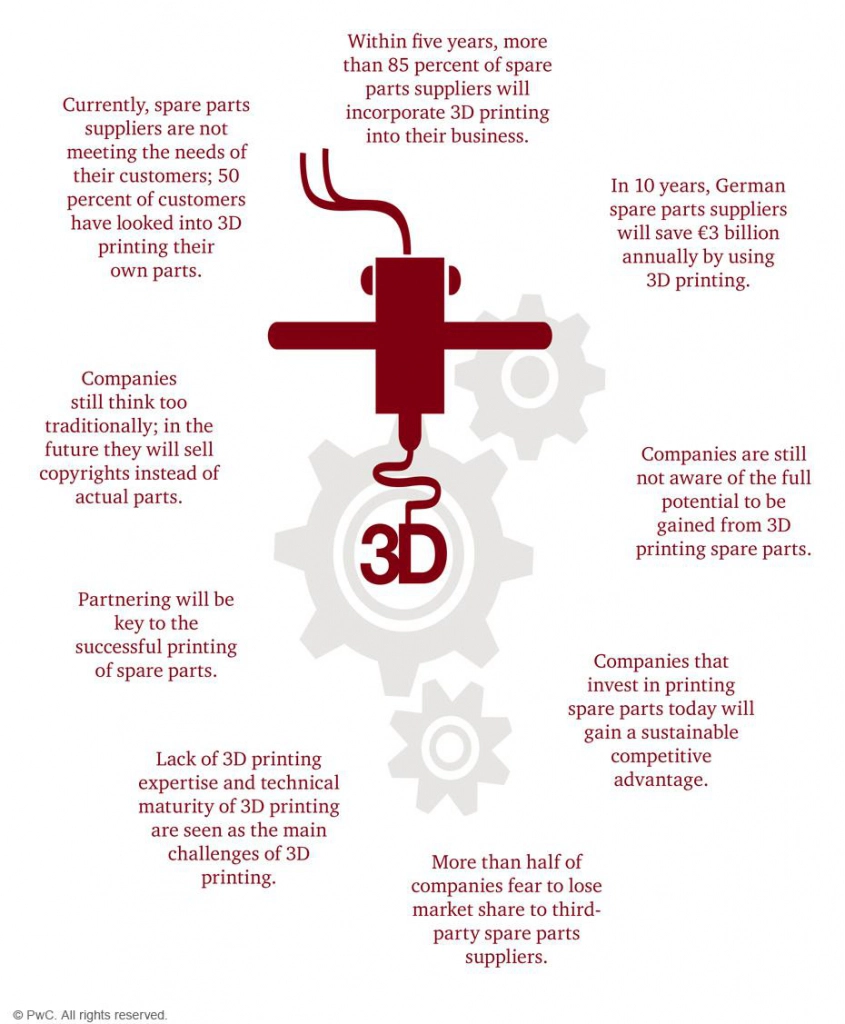
Strategy & part of PWC, has reported that more than 85% of spare parts suppliers will embrace 3D Printing by 2022 in their report “The future of spare parts is 3D: A look at the challenges and opportunities of 3D printing”.
TARIFFS, BORDERS AND THE SHIPPING INDUSTRY BECOME LESS RELEVANT
Even as politicians fight 20th-century-style trade wars with questionable efficacy and unforeseen consequences, geographic borders continue to effectively evaporate. In the coming years, this will make not only tariffs but also the shipping industry less and less relevant. More effective additive manufacturing will enable faster and more easily deployed manufacturing supply chains that circumvent international borders and lower consumer costs dramatically.
By way of example, consider a U.S.-based manufacturer in desperate need of a proprietary replacement part from a Chinese firm. In 2018, that part may have needed to be shipped from China to the U.S., incurring tariffs and delaying production on the U.S. side by days or even weeks. In 2019, this part may be printed on-site in the U.S., with instructions and files delivered digitally from the Chinese firm to the U.S. The end result is the same: The part becomes available. But the process is radically different — certainly from a logistical point of view but, more dramatically, even from a regulatory perspective.
We’re already seeing the first sparks of this transformation in the automotive industry. As materials grow in sophistication and availability, I expect to see the double-digit growth predicted by Frost & Sullivan in the aerospace industry to spread to other industries, too.
Source: Forbes article “What 3D Printing Will Look Like In 2019”
To prepare for the road ahead, spare-part suppliers and logistics companies have started working with companies such as Immensa Technology Labs, Siemens, and 3yourmind to digitize their inventories and build the process of on-demand spare-part production. Companies such as Immensa Technology Labs and others offer the tools for creating digital spare-parts inventories and build the 3D printing capabilities for their partners.
Source: The future of spare parts is 3D: A look at the challenges and opportunities of 3D printing
BENEFITS OF 3D PRINTING SPARE PARTS
- Reduce lead time: Spare parts can be manufactured easily and quickly within the company’s premises.
- Increase spare parts availability: With 3D printing, firms can always make any spare part whenever they need it. There’s no rarity of spare parts for firms with 3D printers.
- Cut costs: 3D printing will cut costs significantly in the production of spare parts. It will reduce the costs of producing, transporting, and storing spare parts.
- Increase customer satisfaction: Currently, industries have to rely on spare part manufacturers to meet their spare part needs. This might sabotage the companies and hurt the relationship with their customers due to delays. 3D printing will help companies to meet customers’ needs and hence increase their satisfaction.
- Competitive advantage: Firms that will adopt 3D printing of spare parts will earn a competitive edge over others who will still rely on third-party suppliers to meet their spare part needs.
3D technology is disrupting all major industries and it will transform how companies handle spare parts to a large extent and solve many of its problems. 3D printing will play a vital role in the evolution of Dubai as a global hub. We expect to see many of the organizations based out of Dubai transform their presence from just warehousing and regional re-export to production hubs for servicing their regional businesses.